
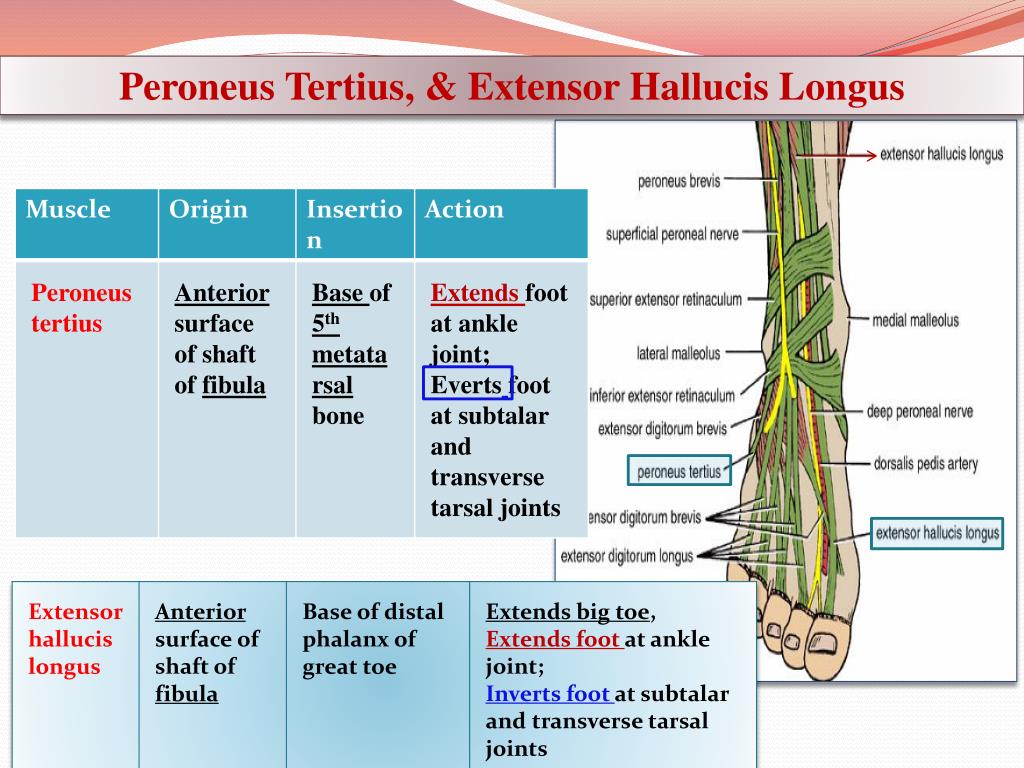
Without a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients, nerve and muscle cells can be damaged. Blood flow to muscle and nerve cells is disrupted.

Because the fascia does not stretch, this can cause increased pressure on the capillaries, nerves, and muscles in the compartment. © American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2003.Ĭompartment syndrome develops when swelling or bleeding occurs within a compartment. Figure B: Reproduced and adapted from The Body Almanac. Rosemont, IL, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2000. The area between the knee and ankle has four major muscle compartments: anterior, lateral, superficial posterior, deep posterior.įigure A: Reproduced and adapted with permission from Gruel CR: Lower Leg, in Sullivan JA, Anderson SJ (eds): Care of the Young Athlete. The role of the fascia is to keep the tissues in place, and, therefore, the fascia does not stretch or expand easily. Covering these tissues is a tough membrane called a fascia. It is most often caused by athletic exertion.Ĭompartments are groupings of muscles, nerves, and blood vessels in your arms and legs. Without treatment, it can lead to permanent muscle damage.Ĭhronic compartment syndrome, also known as exertional compartment syndrome, is usually not a medical emergency. This pressure can decrease blood flow, which prevents nourishment and oxygen from reaching nerve and muscle cells.Ĭompartment syndrome can be either acute or chronic.Īcute compartment syndrome is a medical emergency.
Compartment syndrome is a painful condition that occurs when pressure within the muscles builds to dangerous levels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
